An inflammatory response is a component of the immune response in the human body. The reaction is typically triggered by internal and external factors, but the common trigger is when microorganisms venture into sites where they do not belong. In the inflammation process, the body’s immune system usually recognizes damaged cells, pathogens, and irritants as it embarks on the healing process.
In response to pathogens, harmful microbes, and dangerous chemical reactions, the normal biological response from the body is that it will attempt to remove the pathogenic microbes. After the inflammatory response process is initiated, it often proceeds following a certain course of events up to the point where the source of inflammation is annihilated. Typically, the body would not have the ability to heal wounds, infections, or tissue damage without the occurrence of an inflammatory response.
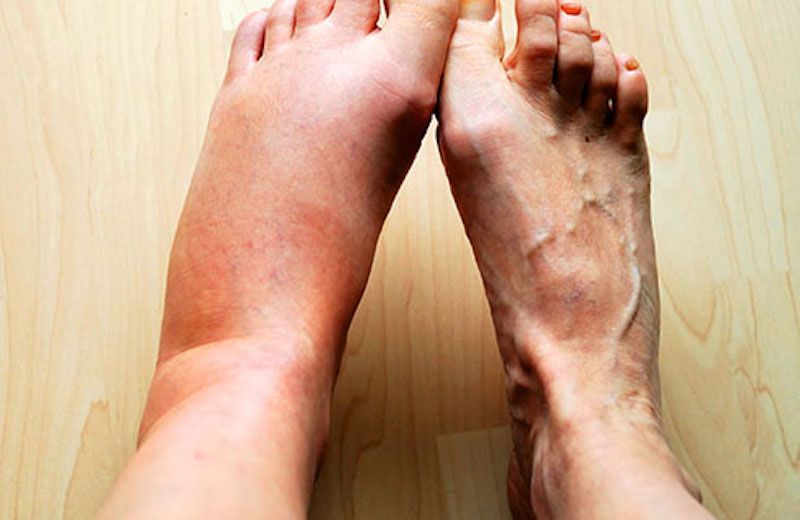
In some cases, inflammation arises when the immune system fights against its own cells by mistake thus causing harmful responses. For example, there are conditions that cause inflammatory effects such as psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, or Crohn’s disease. The main symptoms of inflammation include immobility, pain, redness, heat, or swelling. Pain is usually caused by chemicals that stimulate nerve endings, and subsequently, cause a sensitive feeling in the area. Additionally, swelling is a factor caused by the accumulation of fluid. With the influx of blood to the affected area of the body, the blood causes a characteristic redness and produces heat.
During inflammatory responses, immune cells release different compounds known as the inflammatory mediators. The inflammatory mediators typically include tissue hormones such as histamine or bradykinin. Such compounds cause expansion of the blood vessels in the tissue and allow blood to reach the affected tissue. Inflammatory mediators also lead to an increase in permeability of the narrow vessels to allow more defense cells to enter the affected area. In the event that the inflammation worsens, then the result is sepsis. Sepsis arises when bacteria in the affected area multiply rapidly and increase in the bloodstream in large quantities. There are various causes of inflammation and this article delves into some of the common causes.
1. Bacteria in the Gut
There are inestimable types of bacteria found in the gut. Some of the bacteria are harmless while others are pathogenic. The harmless bacteria are essential in the digestion process while the harmful bacteria lead to various diseases. In optimum conditions in the gut, the good bacteria break down fiber such as inulin and pectin to produce short chain fatty acids. In such harmonious conditions, gut inflammation is suppressed and levels of multiple health biomarkers such as insulin and lipids stabilize.
However, bacteria overgrowth often results when the bacteria in the gut are compromised. In some cases, the bad bacteria overcome the good bacteria. One of the roles of normal/good gut flora is to act as physical barriers against foreign bacteria. Therefore, if the good gut bacteria are disrupted and destabilized, the pathogenic bacteria multiply and cause gut inflammation.
2. Weight
Weight gain and obesity are among the numerous pathological conditions which affect the body. Fat cells often lead to chronic inflammatory responses. As an individual gains weight, the fat cells enlarge beyond their usual capacity as they aim to store excess calories in the form of fat. Subsequently, the enlargement evokes inflammation. In the process, the cells send signals that activate the immune system leading to chronic inflammation.
If the individual embarks on a weight loss program, and the cells shrink to normal size, then the weight loss turns off the signals that trigger chronic inflammation. Additionally, researchers discovered that the Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha and lectin are secretory products of adipocytes which have been linked to adiposity. Essentially, obesity and weight gain lead to a form of systemic inflammation. Weight gain is also associated with insulin resistance that tends to cause inflammatory effects.
3. High Sugar Diet
Studies posit that high sugar diets cause obesity, increased gut permeability, and low-grade inflammatory responses. For example, in one research study, participants were given a can of 375ml soda every day. Eventually, at the end of the study, it emerged that there was an increase in inflammatory markers. For individuals in the study who consumed diet soda without sugar, there was no increase in inflammatory markers. Therefore, it is evident that sugary drinks lead to a spike in inflammatory effects.
Also, consuming excessive amounts of refined carbohydrates is linked to increased inflammation in the body. Further, studies show that a combination of foods with sugar and protein leads to the production of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) in the blood. An increased level of such compounds causes oxidative stress and leads to inflammation. Also, with the increased permeability of the gut, it facilitates bacteria, undigested food, and toxins, to cross the gut barrier and enter the bloodstream causing inflammation.
4. High Salt Diet
Researchers posit that excessive salt intake leads to various negative effects. For example, high salt diets often lead to tissue inflammation and have also been shown to exacerbate autoimmune diseases. In one research, it was determined that patients with myocardial infarctions or hypertension are adversely affected by high sodium intake. The high sodium diet often leads to increased inflammatory responses.
Also, C-reactive protein (CRP), produced in a high salt diet, is a marker of systemic low-grade inflammation. Therefore, a diet that is high in salt increases the level of inflammation markers resulting in inflammation. Elevation of the plasma sodium is thus a predisposing factor to inflammatory effects.
5. Fried Foods
Deep-fried foods are among the foods with the highest levels of advanced glycation endproducts (AGEs). As previously mentioned, AGEs are linked to increased oxidative stress and various inflammatory effects. With an example of cooked chicken, studies have shown that deep fried chicken breast ends up having over nine times the level of AGEs in chicken breast boiled for one hour.
Frying foods has been shown to alter the chemical structure of oils due to hydrogenation and oxidation. Consequently, the level of unsaturated fats decreases while the trans-fatty acids increase. Various toxic compounds also increase with re-use of cooking oil. Further, the high levels of bad cholesterol, common with fried foods leads to higher levels of the C-reactive protein which is a marker of inflammation.
6. Dairy
Dairy products typically have a combination of various nutrients as well as fats. Studies show that the high concentrations of saturated fat, as well as the dietary antigens in dairy products, are linked to the development of chronic inflammatory disorders. Also, such components also lead to various autoimmune diseases.
Autoimmune diseases have the potential to cause inflammatory effects as the body fights its own cells. Research also shows that the saturated fatty acids in dairy products are linked to the activation of pro-inflammatory markers. Consequently, dairy products can lead to the occurrence of inflammatory markers due to the various antigens contained in the foods.