Blood clots occur when the blood thickens becoming more gelatinous. Just as a scab heals after cutting your finger, a blood mass moving in your bloodstream refers to a blood clot. Clotting is however normal for the blood since it’s part of the natural healing process. Unfortunately, it becomes dangerous when the blood clot occurs in any part of the body.
The blood clot is pumped in the veins of the legs, arms, brain, or any other body organ, can, however, get stuck blocking tissues. This causes the leg to start dying slowly due to loss of blood that is rich in oxygen.
These may not sound life threatening, but blood clots that develop in the leg’s deep veins, if not treated within few hours, it may detach then travel through the bloodstream to the lungs or heart, which can cause a severe pulmonary embolism (PE) or even death. In most instances, blood clots in the leg form because of long durations of travel, with no or few opportunities of stretching your legs and walk around.
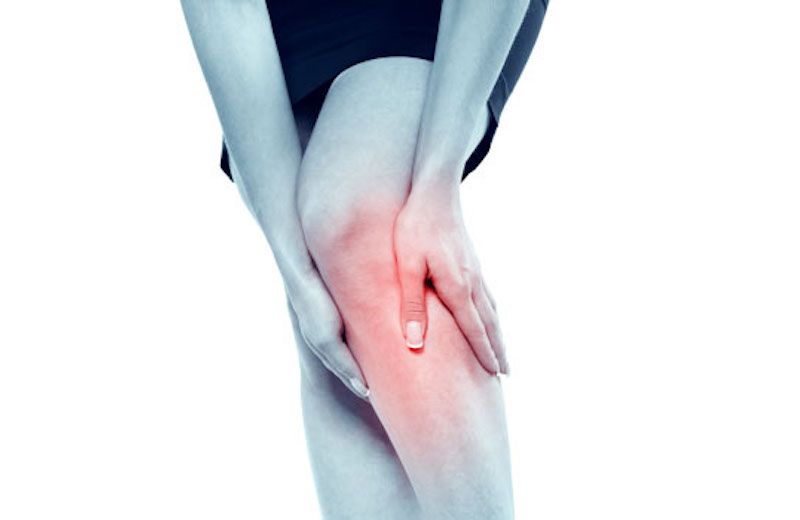
Below are 7 signs that you may be having a dangerous blood clot in the leg:
1. Leg Pain
With massive blood clots, severe pain can occur in the affected leg. The pain is often around the ankle, foot, or leg. It happens when there is pressure administered to the vein around the blood clot. Pain is felt around the surface veins of the leg, leading to difficulty in any movement. It happens especially when walking, standing, climbing stairs, or during exercising. Most patients who experience lots in one or both legs say they felt cramps which were similar to charley horse. Such severe is caused by DVT blood clot formed in the inner vessel.
Moving the legs around after sitting for too long also helps in keeping the blood flowing. Walking from time to time after a bed rest can also prevent clots from forming in your legs. Additionally, blood thinners during surgery, as prescribed by your doctor, can as well lower the chances of developing painful blood clot later in life which mostly happens in the legs. Specialized attention is advised to precisely tell if it’s a clot causing the pain in the leg.
2. Swelling
Any pressure on veins behind the blood clot, can lead to the build and pushing outwards as well as stretching of the tissues causing swelling. Tumors which in most cases are very painful may occur in the area around the clot, especially if it’s in the leg, ankle or the calf area. These body areas have increased tissue and bone densities. Therefore, it makes it difficult for your body to clear the forming clot naturally. Swelling related to blood clotting may not respond to treatments such as an application of cold or hot compresses. The swelling may intensify for no apparent reason, and no external injury may have occurred.
3. Redness
Slight discoloration on the skin of the affected area is often the first signs of a clot deep in the vein. It is caused by lack of sufficient blood supply to the affected area. It is also caused by a dense collection of the blood beneath the skin, therefore the redness becoming visible as their sizes increases. If you persistently experience red patches on your leg, particularly after a surgery or an injury, you should immediately inform your doctor. The primary indication of a cot deep in the vein of the leg is skin redness that doesn’t go away or intensifies for no reason.
4. Chest Pain
Experiencing chest pains is a common reason why people visit the hospital for specialized attention. Chest pains vary depending on many factors.
Often, this particular pain feels like a weighty object that is causing pressure on your chest or still a dull piercing pain. Blood clots can lead to sharp pains in the chest caused by restricted breathing. Particularly when the blood clot detaches itself it settles in the lungs. In this case, you may be experiencing lung-related chest pain. Your doctor may run tests to help in the diagnosis as well as treatment.
5. Panting
It is experiencing short, and quick breaths. Panting, quickening of the pulse rate as well as breath shortness, are some of the symptoms experienced when clots enter the chest or lungs area (pulmonary embolism). Panting may occur when there is no sufficient air penetrating the lungs. That happens when a clot settles in the lungs obstructing the normal flow of adequate air. Panting may lead to an increase in pulse rate, therefore causing discomfort, pounding, fluttering, or pain in your chest. Medical attention is advised to diagnose the cause of the gasping.
6. Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath feels as if you are unable to breathe, racing pulse, fever, sweating, and coughing blood are signs of a clot in the lungs. Shortness of breath is a symptom of pulmonary embolism, caused by a blood clot positioned deep in your lungs. Together with other indications of a blood clot in the vein, shortness of breath should be immediately investigated by your doctor as this is life-threatening. It’s critical for a person to seek doctors’ attention as soon as possible, especially with symptoms of blood clots in the heart, lungs, brain, and abdomen.
7. Coughing
Sudden as well as unexplained bloody cough may occur if there is a blood clot positioned in your lungs, which had previously detached from a vein. Coughing out blood should be very alarming, whether in small or large amount. Coughing blood is quite often a symptom of a particular illness. You can discharge blood from the throat, nose, lungs, or the upper airways. The seriousness depends on the amount of blood and the duration of time the bloody cough has been happening. You should consult your doctor as quickly as possible if you are experiencing this bloody cough.